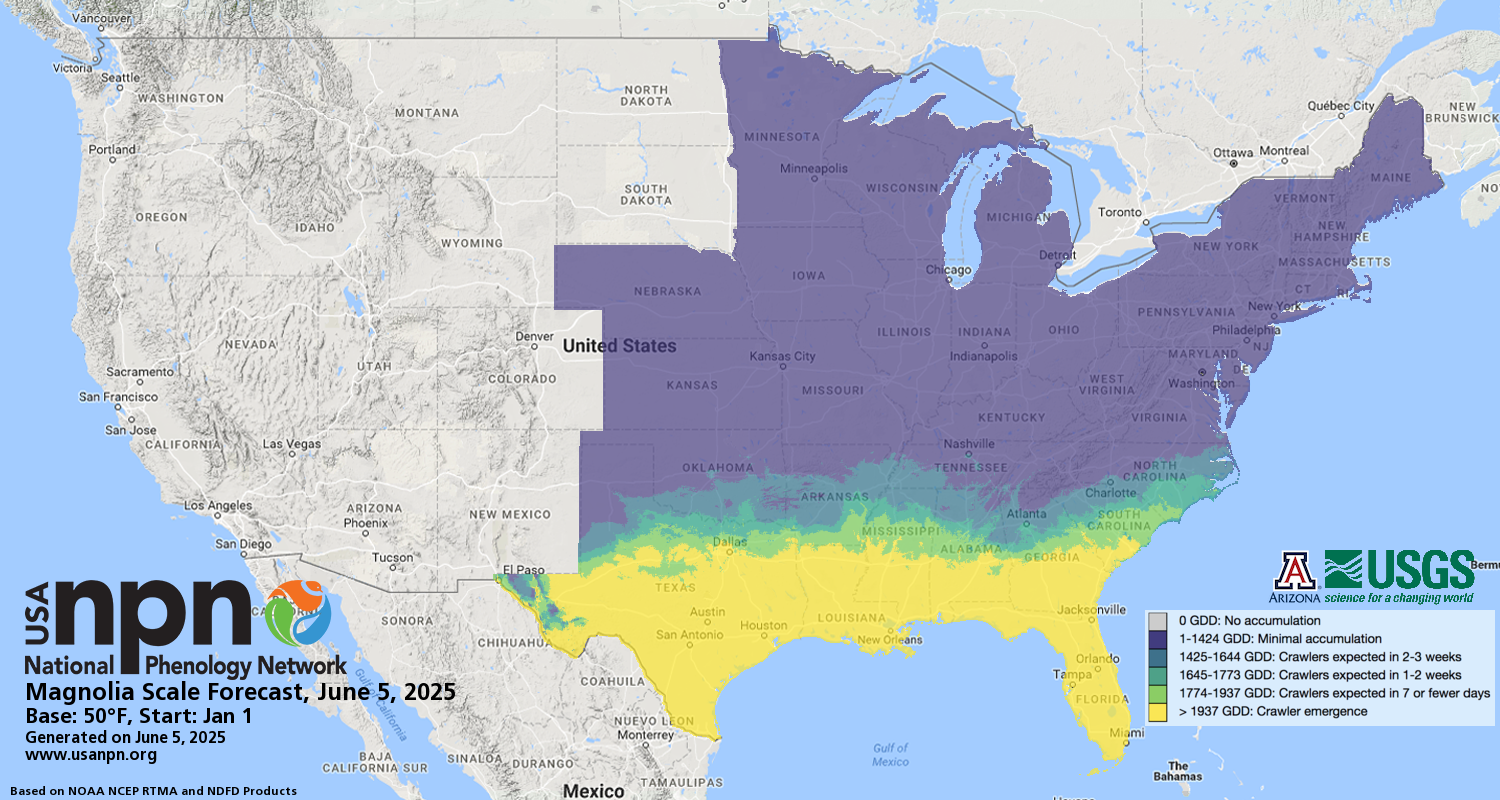
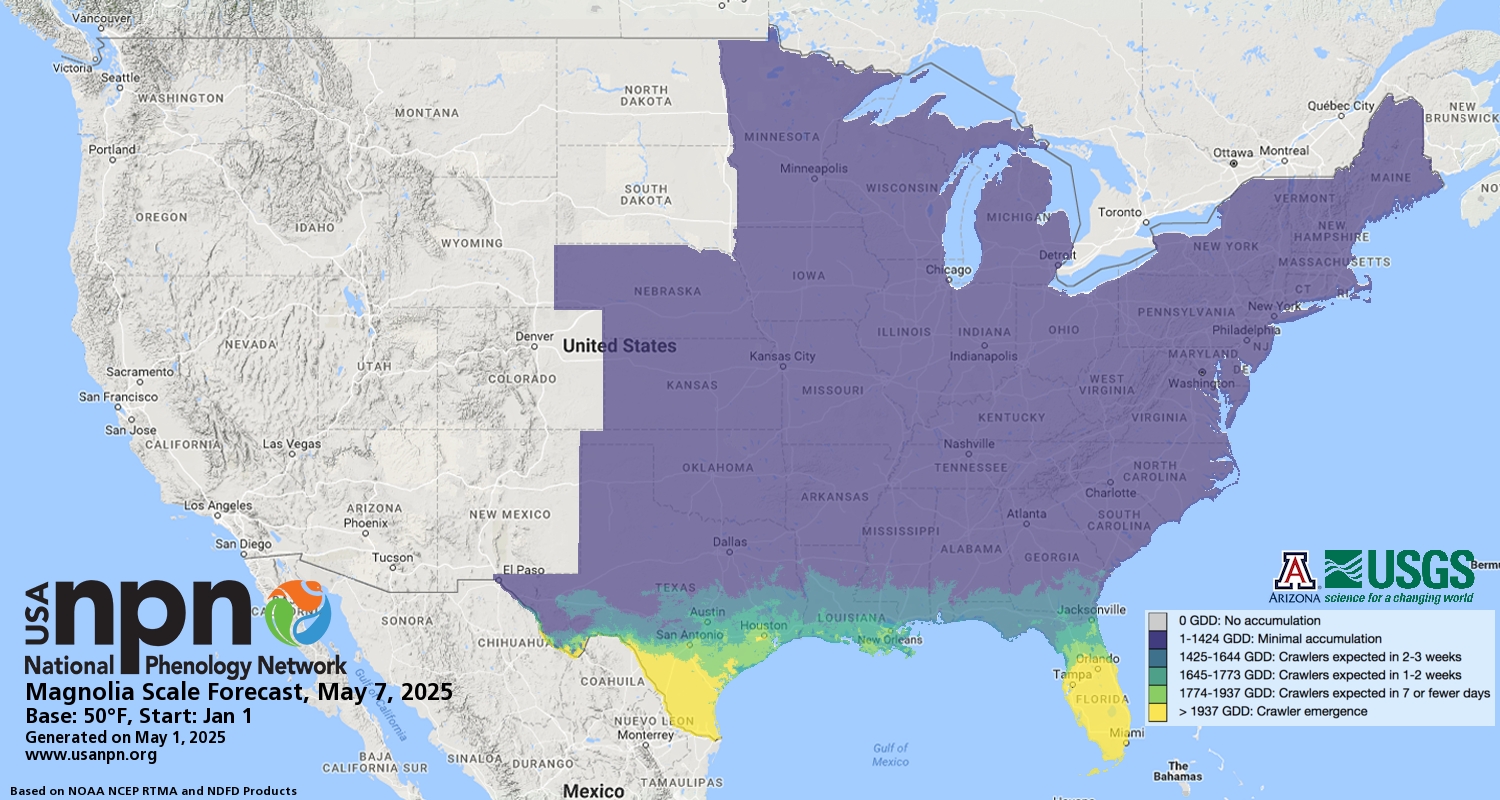
Due to technical difficulties, this Pheno Forecast is not currently being updated for 2025. Please check back next year for updated map status.
Magnolia scale is a pest native to the Eastern United States that affects magnolia trees and tulip trees. They cause stress to their host trees by removing sap which can lead to yellowing leaves, twig dieback, and even death.
WHAT ARE PHENO FORECASTS?
Pheno Forecast maps predict key life cycle stages in invasive and pest species, to improve management efficacy. For insect pest species, Pheno Forecasts are based on published growing degree day (GDD) thresholds for key points in species life cycles. These key points typically represent life cycle stages when management actions are most effective. These maps are updated daily and available 6 days in the future.
Help us improve these maps! Our Pheno Forecast map products are still in development, and we seek input on their performance in your area. Give your feedback at the bottom of the page.

SPECIES BACKGROUND
Native to the eastern U.S., magnolia scale (Neolecanium cornuparvum) specializes on magnolia trees and tulip trees and is one of the largest soft scale insects in North America, reaching up to 0.5 inches in length. The scale spends the winter as small dark nymphs, but during the spring they begin to feed, grow, and change color to a brown-purple color. Crawlers emerge after hatching internally from adults in late summer into early fall. This is the stage when the insects are most vulnerable to treatment.

CRAWLER FORECAST
We forecast crawler emergence based on growing degree days. Treatments are often applied when crawlers emerge from their eggs and before they develop their protective waxy coating. For specific information on preferred treatment options in your region, we recommend contacting your local extension agent. Additional treatment resources are available through the Morton Arboretum and Penn State Extension.
EXPLORE THIS FORECAST
Learn more about this forecast using our visualization tool!
|
Phenophase |
GDD threshold |
Base temp |
Start date |
GDD method |
Model origin |
Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Crawler emergence |
1938oF |
50oF |
Jan 1 |
Double sine |
MI |
More information on map development and re-use policy.