Emerald ash borer is a beetle that causes significant harm to ash trees throughout the eastern United States.
WHAT ARE PHENO FORECASTS?
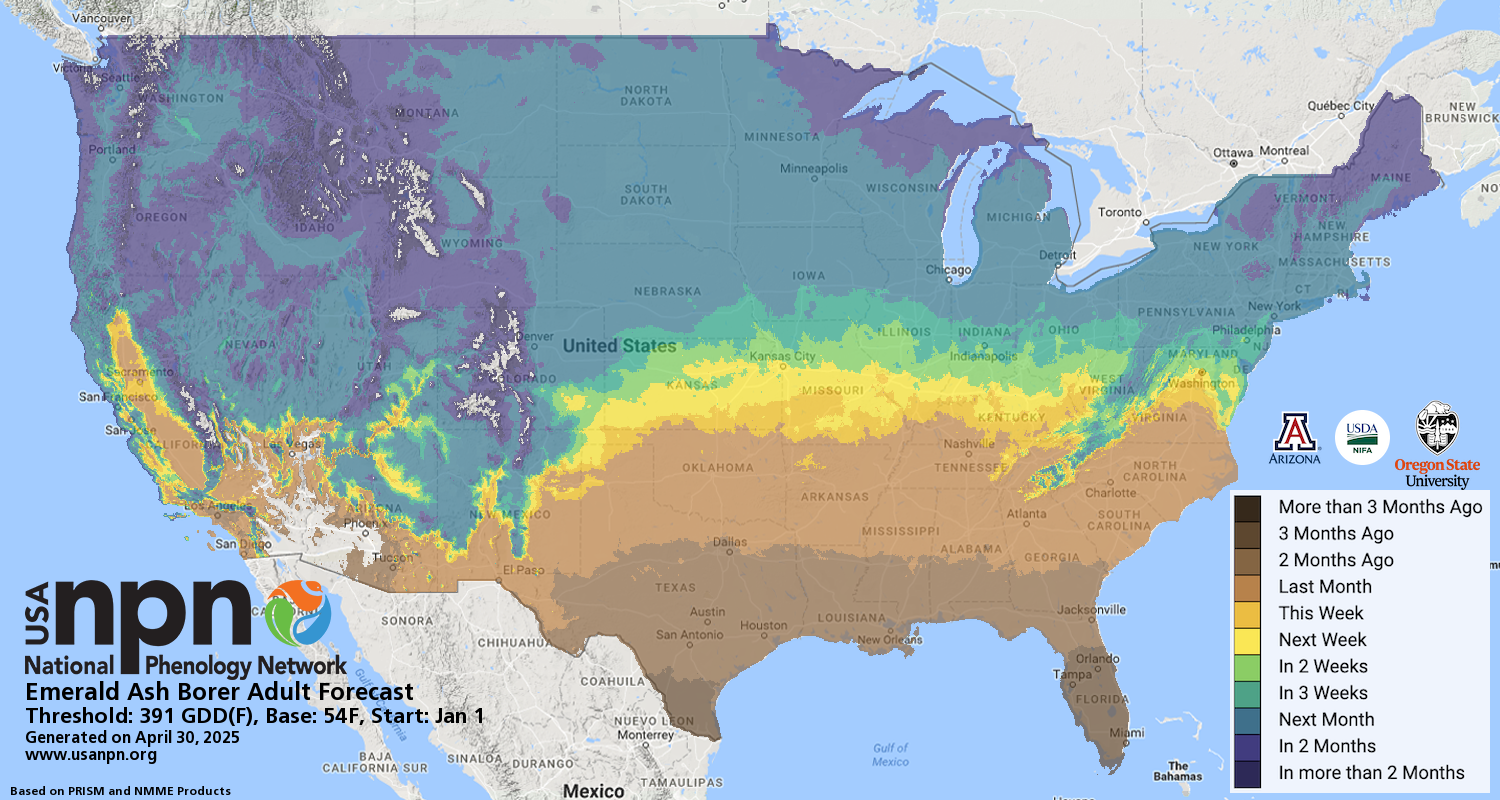
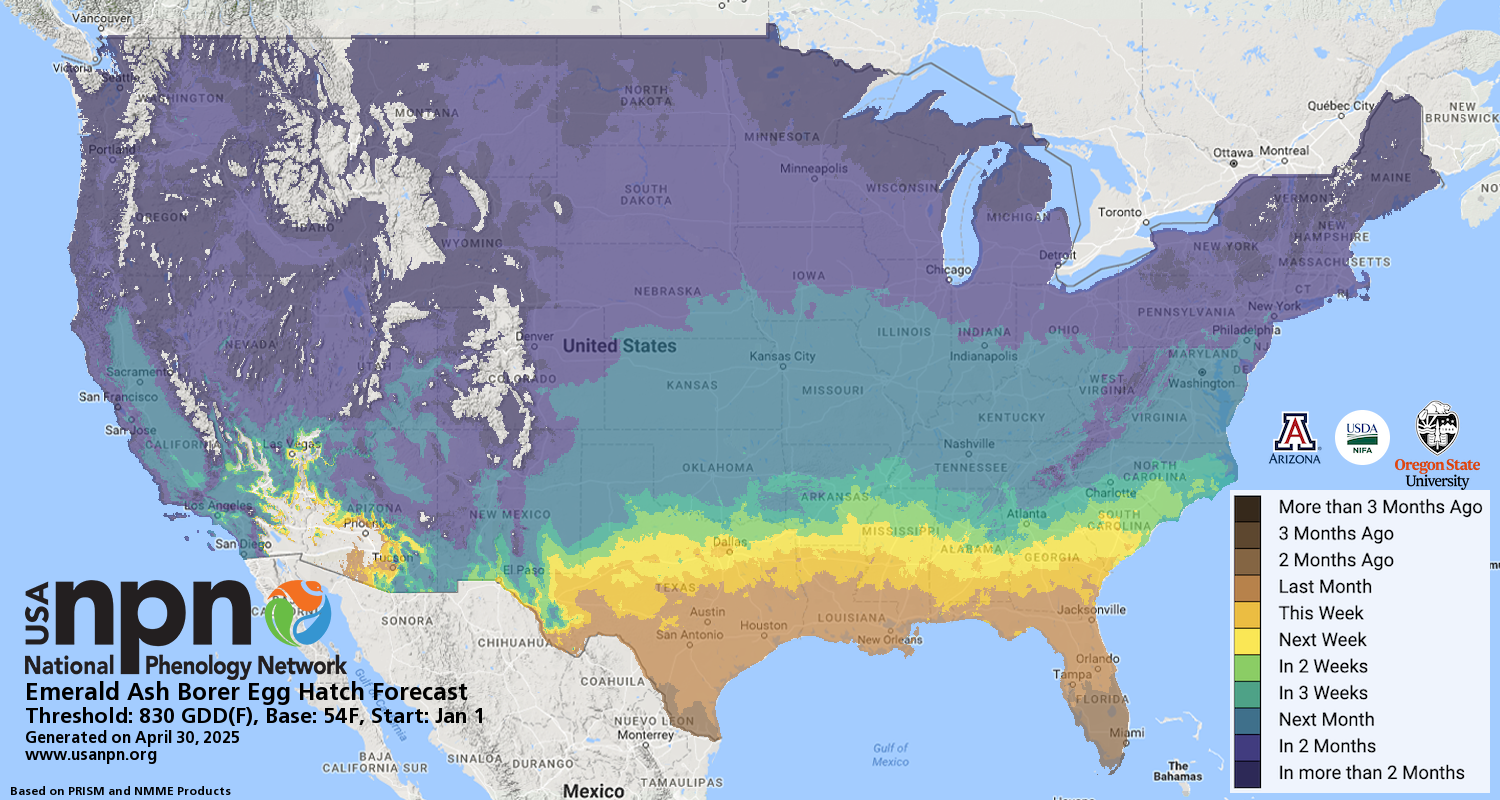
Pheno Forecast maps predict key life cycle stages in invasive and pest species, to improve management efficacy. For insect pest species, Pheno Forecasts are based on published growing degree day (GDD) thresholds for key points in species life cycles. These key points typically represent life cycle stages when management actions are most effective. For Emerald Ash Borer, we forecast the first emergence of adults and the earliest egg hatch in the spring, for the full calendar year. Watch a video on how to use the EAB Pheno Forecast.
Help us improve these maps! Our Pheno Forecast map products are still in development, and we seek input on their performance in your area. Give your feedback at the bottom of the page.
SIGN UP FOR PHENO FORECAST NOTIFICATIONS!
Sign up to be notified by email approximately two weeks and again six days ahead of key growing degree day thresholds for species of interest at your location

SPECIES BACKGROUND
Emerald Ash Borer (Agrilus planipennis) is non-native beetle from Asia which has spread across the eastern United States since 2002. In their larval stage, the beetles destroy the heartwood of ash trees, killing them within a few years. The pest is responsible for the death of hundreds of millions of ash trees.
LEARN HOW TO OBSERVE PHENOLOGY OF EAB
Our learning module walks you through how to identify EAB, how to report its life cycle events, and why you should care.

ADULT AND EGG HATCH FORECAST
We forecast adult emergence and egg hatch based on growing degree days. The forecasts are available for the contiguous United States, except for those areas where the temperatures for the current year are expected to be either too extreme for EAB to survive or too cold for a life cycle event to occur. Treatments are applied to control for adult beetles on infested trees, to reduce the spread of the pest. Adults lay eggs approximately 14 days after emergence, so treatment is critical in this window. Knowing when these eggs hatch helps managers know when larvae are active in the tree. For specific information on preferred treatment options in your region, we recommend contacting your local extension agent. For more information on treatment guidance, visit Insecticide Options for Protecting Ash Trees from Emerald Ash Borer or Emerald Ash Borer Information Network.
EXPLORE THIS FORECAST
Learn more about this forecast using our visualization tool!
| Phenophase | GDD threshold | Base temp | Upper threshold | Start date | GDD method | Model origin | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult Emergence (earliest date that overwintering individuals are expected to emerge as adults) | 391oF | 54oF | 97oF | Jan 1 | Single triangle | OH, MI | DDRP, Duarte 2014, and Barker et al 2023 |
| Egg Hatch (earliest date that overwintering eggs are predicted to hatch) | 830oF | 54oF | 97oF | Jan 1 | Single triangle | OH, MI | DDRP, Duarte 2014, and Barker et al 2023 |
The development of this forecast was funded primarily by USDA NIFA AFRI TSAB Award #2022-68013-37138 to support agricultural biosecurity.
Learn more about the forecast in a presentation hosted by Emerald Ash Borer University.
More information on map development and re-use policy.